Spreadsheet software — led by products like Microsoft’s Excel, Google’s Sheets and Apple’s Numbers — continues to be one of the most-used categories of business apps, with Excel alone clocking up more than a billion users just on its Android version. Now, a startup called Rows that’s built on that ubiquity, with a low-code platform that lets people populate and analyze web apps using just spreadsheet interfaces, is announcing funding and launching a freemium open beta of its expanded service.
The Berlin-based startup — which rebranded from dashdash at the end of last year — closed a Series B round of $16 million, money that it is using to continue investing in its platform as well as in sales and marketing. The platform’s move into an open beta comes with some 50 new integrations with other platforms like LinkedIn, Instagram and more, as well as 200 new features (using known spreadsheet shortcuts) to use in them.
The round was led by Lakestar, with past investors Accel (which led its $8 million Series A in 2018) and Cherry Ventures also participating. Christian Reber has also invested in this round. Reber knows a thing or two about software disrupting legacy productivity software — he is the co-founder and CEO of presentation software startup Pitch and the former CEO and founder of Microsoft-acquired Wunderlist — and notably he is joining Rows’ Advisory Board along with the investment.
A little detail about this Series B: CEO Humberto Ayres Pereira, who is based out of Porto, Portugal, where some of the staff is also based, tells us that this round actually was quietly closed over a year ago, in January 2020 — just ahead of the world shutting down amid the Covid-19 pandemic.
The startup chose to announce that round today to coincide with adding more features to its product and moving it into an open beta, he said.
That open beta is free in its most basic form — the free tier is limited to 10 users or less and a minimal amount of integration usage. Paid tiers, which cover more team members and up to 100,000 integration tasks (which are measured by how many times a spreadsheet queries another service), start at $59 per month.
One strong sign of interest in this latest iteration of the software is the lasting popularity of spreadsheets. Another is Rows’ traction to date: in invite-only mode, it picked up 10,000 users off its waitlist, and hundreds of companies, as customers. Currently most of those are free, Ayres Pereira said.
“Our goal is to have 1,000 paying companies as customers in the 12 months,” he said. That process has only just started, he added, with paying numbers in the modest “dozens” for now. He emphasized though that the company is very cash efficient and has, even without raising more funding, two years of runway on the money it has in the bank now.
The growing appeal of low-code
No-code and low-code software, which let people create and work with apps and other digital content without delving deep into the lines of code that underpin them, have continued to pick up traction in the market in the last several years.
The reason for this is straightforward: non-technical employees may not code, but they are getting increasingly adept at understanding how services function and what can be achieved within an app.
No-code and low-code platforms let them get more hands-on when it comes to customizing and creating the services that they need to use everyday to get their work done, without the time and effort it might take to get an engineer involved.
“People want to create their own tools,” said Ayres Pereira. “They want to understand and test and iterate.” He said that the majority of Rows’ users so far are based out of North America, and typical use cases include marketing and sales teams, as well as companies using Rows spreadsheets as a dynamic interface to manage logistics and other operations.
Stephen Nundy, the partner at Lakestar who led its investment, describes the army of users taking up no-code tools as “citizen developers.”
Rows is precisely the kind of platform that plays into the low-code trend. For people who are already au fait with the kinds of tools that you find in spreadsheets — and something like Excel has hundreds of functions in it — it presents a way of leaning on those familiar functions to trigger integrations with other apps, and to subsequently use a spreadsheet created in Rows to both analyse data from other apps, as well as update them.
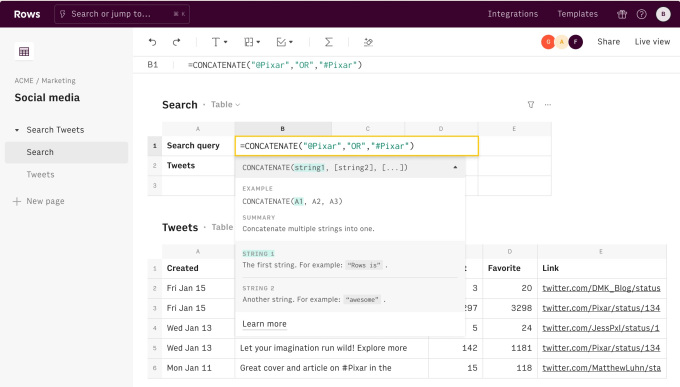
You might ask, why is it more useful, for example, to look at content from Twitter in Rows rather than Twitter itself? A Rows document might let a person search for a set of Tweets using a certain chain of keywords, and then organise those results based on parameters such as how many “likes” those Tweets received.
Or users responding to a call to action for a promotion on Instagram might then be cross referenced with a company’s existing database of customers, to analyze how those respondents overlap or present new leads.
You might also wonder why existing spreadsheet products may not have already build functionality like this.
Interestingly, Microsoft did dabble in building a way of linking up Excel with some rudimentary computing functions, in the form of Visual Basic for Applications. This however reached the dubious distinction of topping developers’ “most dreaded” languages list for two years running, and so as you might imagine it has somewhat died a death.
However, it does point to an opportunity for incumbents to disrupt their disruptors.
Apart from those most obvious, entrenched competitors, there have been a number of other startups building tools that are providing similar no- and low-code approaches.
Gyana is focusing more on data science, Tray.io provides a graphical interface to integrate how apps work together, Zapier and Notion also provide simple interfaces to integrate apps and APIs together, and Airtable has its own take on reinventing the spreadsheet interface. For now, Ayres Pereira sees these more as compatriots than competitors.
“Yes, we overlap with services like Zapier and Notion,” he said. “But I’d say we are friends. We’re all raising awareness about people being able to do more and not having to be stuck using old tools. It’s not a zero sum game for us.”
When we covered Rows’s Series A two years ago, the startup had built a platform to let people who are comfortable working with data in spreadsheets to use that interface to create and populate content in web apps. It had a lot of extensibility, but mainly geared at people still willing to do the work to create those links.
Two years on, while the spreadsheet has remained the anchor, the platform has grown. Ayres Pereira, who co-founded the company with Torben Schulz (both pictured above), said that there are some 50 new integrations now, including ways to analyse and update content on social media platforms like Instagram, YouTube, CrunchBase, Salesforce, Slack, LinkedIn and Twitter, as well as some 200 new features in the platform itself.
While people can import into Rows data from Google Sheets, he noted that the big daddy of them all, Excel, is not supported right now. The reason, he said, is because the vast majority of users of the product use the desktop version, which does not have APIs.
Meanwhile, Rows also has a number of templates available for people to guide them through simple tasks, such as looking up LinkedIn profiles or emails for a list of people; tracking social media counts and so on.
One of the most common aspects of spreadsheets, however, has yet to be built. The interface is still banked around rows and columns, but with no graphical tools to visualize data in different ways such as pie charts or graphs as you might have in a typical spreadsheet program.
It’s for this reason that Rows has yet to exit beta. The feature is one that is requested a lot, Pereira admitted, describing it as “the final frontier.” When Rows is ready to ship with that functionality, likely by Q3 of this year, it will tick over to general “1.0” release, he added.
“Humberto and Torben have really impressed us with their ambition to disrupt the market with a new spreadsheet paradigm that tackles the significant shortcomings of today’s solutions,” said Nundy at Lakestar. “Data integrations are native, the collaboration experience is first class and the ability to share and publish your work as an application is unique and will create more ‘Citizen developers’ to emerge. This is essential to the growing needs of today’s technology literate workforce. The level of interest they’ve received in their private beta is proof of the desirability of platforms like Rows, and we’re excited to be supporting them through their public beta launch and beyond with this investment.” Nundy is also joining Rows’ board with this round.
